GIA Diamonds
Diamond Grading & GIA Certified Diamonds
A special Unique cut for every occasion
Each diamond has a unique composition because of its exposure of a variety of elements during its growth including pressure, heat, and the presence of other elements. These distinct features give the diamond its visual appeal and can be summed up by the Four C’s of diamond grading: cut, clarity, color and carat.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is credited with standardizing the grading industry by introducing the aforementioned Four C’s. The GIA was established in 1931 and it is the world’s foremost authority on diamonds, colored stones, and pearls. Today, the Four C’s are the universal method for assessing the quality of any diamond, anywhere in the world.
The Four C’s of Diamond Quality
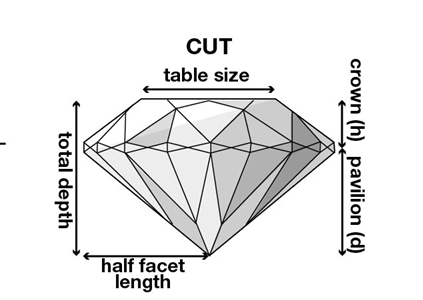
The Cut
The cut grade reflects how well the facets interact with light. Of the 4C’s, the cut is responsible for the diamond’s beauty. A diamond that has been expertly cut will reflect light beautifully and increase the diamonds sparkle. The more precise the cut, the more captivating the diamond is to the eye.
The GIA Cut Grading System evaluates seven components when it comes to cut. The first three, brightness, fire, and scintillation, consider the diamond’s overall face-up appearance. The remaining four, weight ratio, durability, polish, and symmetry, assess a diamond’s design and craftsmanship.
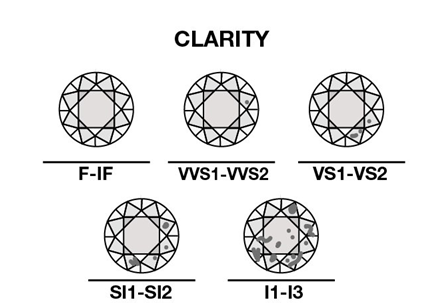
The Clarity
The organic process of tremendous heat and pressure that creates diamonds also leaves them with internal inclusions and surface blemishes. Diamonds without inclusions or blemishes are rare; however, most characteristics can only be seen with magnification.
The GIA clarity scale has six categories including Flawless, Internally Flawless, Very Very Slightly Included, Very Slightly Included, Slightly Included, and Included. Some of these categories are divided for a total of 11 specific clarity grades.
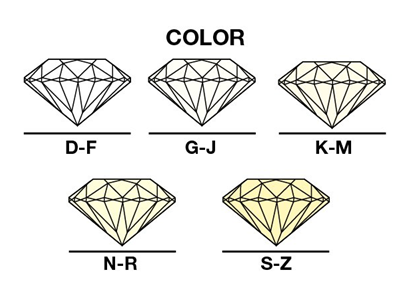
The Color
Diamond color is graded on what you cannot see, the less color a diamond has – the higher the value. Diamonds exist on a scale of many different shades ranging from white to pale yellow or brown. These subtle differences are graded on a color scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow).
The GIA’s color-grading scale is the industry’s most widely accepted grading system where each letter grade has a clearly defined range of color appearance.
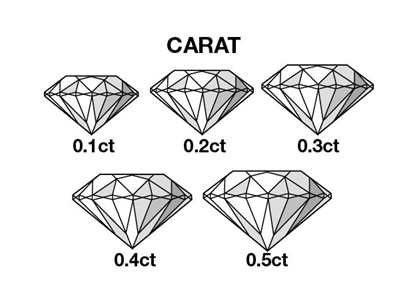
The Carat
Diamonds are weighed in metric carats and one carat is equal to 0.2 grams. Similar to the way a dollar can be divided into 100 pennies, a carat is divided into 100 points. Precise measurements are taken to the hundredth decimal place to ensure complete accuracy as a fraction of a carat can make a considerable difference in cost.
The carat system takes its name from the carob seed. Carob seeds had a uniform weight and were used as counterweights to balance scales by early gem traders. Carob seeds were used as a reference for the weight of individual diamonds.